Antibiotics can be used to treat bacterial infections and diseases.
They kill bacteria by interfering with their metabolism.
- They stop them making new cell walls when they divide, so the cell takes in water by osmosis and bursts.
- The stop bacteria making proteins. They interfere with their ribosomes and so protein synthesis cannot happen.
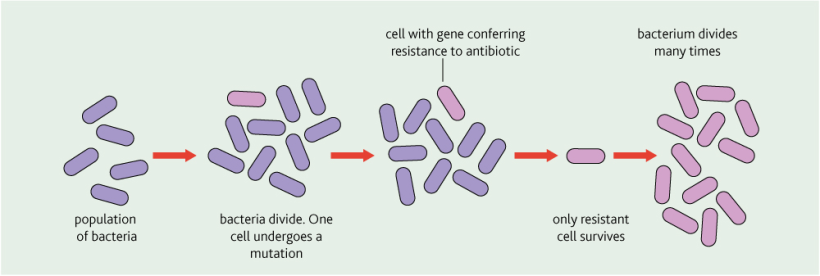
Antibiotic resistance
Some bacteria are resistant to lots of antibiotics – these are multi-drug resistant bacteria.
Antibiotic resistance is more likely to develop when antibiotics are widely used. How can this be stopped:
- Doctors avoid giving antibiotics for minor infections present no danger – if the bacteria are not exposed to the antibiotic resistance is unlikely to develop.
- Doctors should prescribe antibiotics for viral diseases – antibiotics do not destroy viruses, but if bacteria are present, they might develop resistance.
- Always finish the course of antibiotics – there may be a few bacteria left after the illness has gone, these will be the bacteria that are most resistant to the antibiotics, so if you don’t finish, they will survive and multiply, passing on the resistant gene and spread to other people.
MRSA is a well known bacteria. It is resistant to the antibiotic methicillin. Hopsitals take care to avoid spreading MRSA in hospitals:
- contact isolation – wash hands before and after touching patients
- put patients in a separate room if they have it in their nose so they can’t spread by droplet infection
- clean surfaces regularly to eliminate it from dust
- clean beds after a patient has used it
- put MRSA patients together in a separate room
- Staff wear clean disposable aprons and gloves, and throw them away after use
- visitors use alcohol hand rub to sterilise hands before and after visiting